Gaussian law
As a particular example of interest, one can mention the Gaussian radom variables or vectors.
For variable,
 admit the density
admit the density
where the normalisation constant is ignored since it is only present to respect the integral
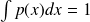
For vectors,
 admit the density
admit the density
With the property that the transform of Gaussian random vector
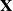 by the linear transform
by the linear transform
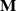 is still a Gaussian random vector
is still a Gaussian random vector
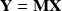
of mean
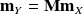
with covariance matrix

Random sample of Gaussian random vector can be constructed following [?] as
where
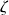 is a Gaussian random noise of covariance matrix
is a Gaussian random noise of covariance matrix
 (that is an ensemble of independent sample of a normalized and centered Gaussian law), and
(that is an ensemble of independent sample of a normalized and centered Gaussian law), and
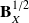 denotes a square-root of this symmetric positive matrix.
denotes a square-root of this symmetric positive matrix.
Example :
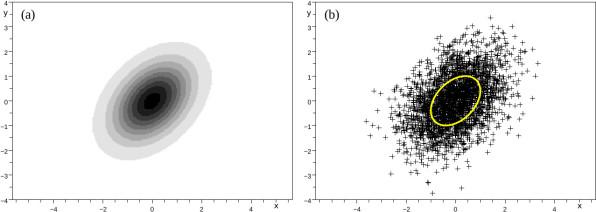
As an example, the following picture represents a 2D-Gaussian law with a discretized version