General formalism
The Baye's rule
The Baye's rule is based on conditional probabilities.
By definition,
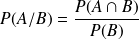
and this is the Baye's rule.
What des it means for our job?
Classical notations for data assimilation have been introduced by [ICGL97], we try to follow them as possible as we can. We denote by
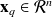 the digital representation of the system (atmosphere, ocean,..) at time
the digital representation of the system (atmosphere, ocean,..) at time
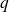
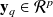 the observations of the system at time
the observations of the system at time
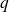 With these notations, the Baye's rule states that
With these notations, the Baye's rule states that
or more simply
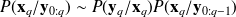 where the normalization term is forgotten. This is called the analysis step.
where the normalization term is forgotten. This is called the analysis step.
If we combine the forecast step and the analysis step, we obtain the following evolution of information:
where
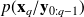 denotes the uncertainty on the state
denotes the uncertainty on the state
 at time
at time
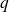 knowing observations until time
knowing observations until time
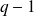 ,
,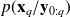 the one for
the one for
 at time
at time
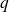 conditionned by the knowledge of the new observations at time
conditionned by the knowledge of the new observations at time
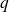 , this is the analysis step
, this is the analysis step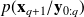 denotes the uncertainty on the state
denotes the uncertainty on the state
 at time
at time
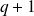 knowing observations until time
knowing observations until time
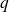 , this is the forecast step
, this is the forecast step
Keep in mind that here, we have three processes:
The real process
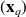 , that is the realization of the system (the weather we are seeing day after days).
, that is the realization of the system (the weather we are seeing day after days).The analysis process
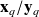 , that is our knowledge of the real process
, that is our knowledge of the real process
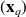 knowing all observations until time
knowing all observations until time
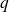 .
.The forecast process
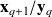 that is the time evolution thanks to the dynamics
that is the time evolution thanks to the dynamics
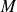 of the analysis process, that is (without model error)
of the analysis process, that is (without model error)
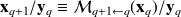 .
.
Optimal states: the analysis
An optimal state is a state that minimizes the variance of error.
It can be shown that
minimize the variance of error that is, if
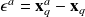 (we assume this random value is centered, that is
(we assume this random value is centered, that is
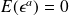
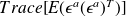 reaches its minimum for
reaches its minimum for
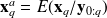 .
.
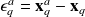 is the analysis error and the matrix
is the analysis error and the matrix
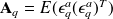 is the analysis covariance matrix.
is the analysis covariance matrix.
Optimal states: the background
Similarly,
is also an optimal estimator at time
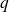 .
.
The error
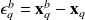 is the forecast error and the matrix
is the forecast error and the matrix
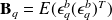 is the forecas error covariance matrix.
is the forecas error covariance matrix.